The External Control Bus inputs (set up on the “Other Controls” tab in Preferences - and in the MIDI In device in the hardware interface) let you send MIDI directly to the individual devices in the rack. This is mainly used if you control Reason from an external sequencer, etc. See “About the External Control Bus inputs”.
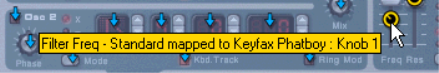
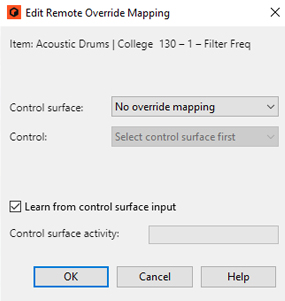
You can also do manual Remote Overrides to assign Reason parameters to knobs/sliders/buttons on your control keyboard/surface, see “Remote Override”.
|
|
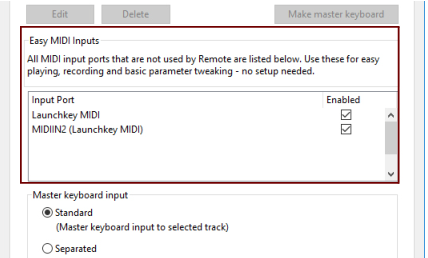
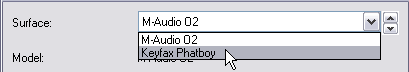
If a MIDI Port of your connected control surface/keyboard is already used by the Easy MIDI Inputs function (see “Automatic set-up using the Easy MIDI Inputs function”), this detection will override this and automatically remove the MIDI In Port from the Easy MIDI Inputs list.
|
MIDI inputs not selected here or on the Sync page (see “Advanced MIDI - The External Control Bus inputs”) are available to other programs.
For example, if you lock a control surface to the Main Mixer, you will always have control over levels, pans and additional channel strip parameters - see “Remote controlling the Main Mixer” and “Remote controlling multiple mixer channels”. You could also have dedicated controls for transport, Undo/Redo, sequencer track MIDI focus selection, etc.
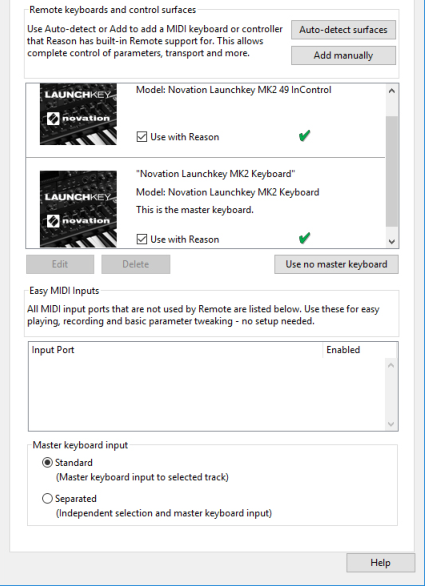
This means that you set Master Keyboard Input to a track in the sequencer to route the control surface(s) to the track’s device in the rack. You can bypass this functionality by locking a control surface to a specific device - see “Locking a surface to a device”. Or you can simply use Remote Override mapping (see “Remote Override” for specific parameters - these will then be mapped to the selected controls regardless of Master Keyboard Input.
E.g. if a Subtractor has Master Keyboard Input, your control surface will control the most important Subtractor parameters. If you set Master Keyboard Input to a track connected to an NN-XT, the control surface will now control parameters on the NN-XT device, and so on for each device. There are standard mapping variations for most devices as well - see “About mapping variations”.
If you do not have transport controls on your control surface you can still map transport controls to controllers using Remote Override mapping - see “Remote Override mapping”.
If you use Remote Override mapping (see “Remote Override”), the overrides will be saved with the current song, but won’t be there if you create a new song.
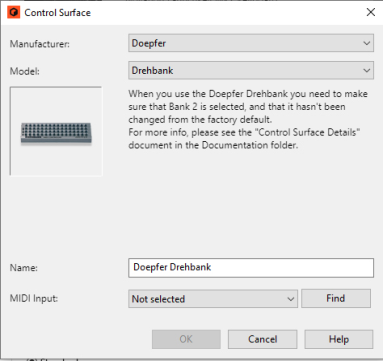
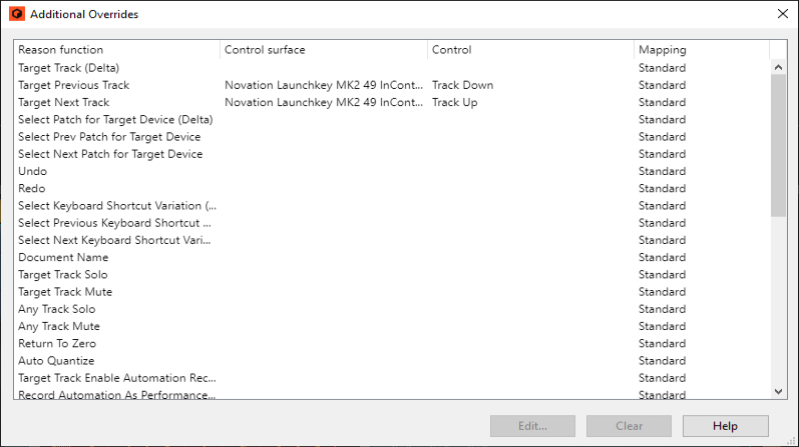
The “Control Surface Details” document contains some information about the standard mappings of the different control surface models. But you can also activate Remote Override Edit mode to see which parameters for each device are mapped to your control surface(s) - see “Remote Override”.
This is not a conflict of any kind, but simply a consequence that stems from the fact that all control surfaces by default follow Master Keyboard Input. By using Surface Locking (see below) or Remote Override (see “Remote Override”) you have full control over your control surfaces.
|
|
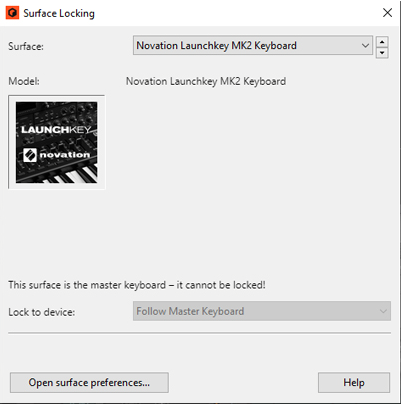
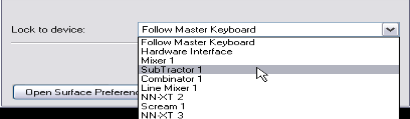
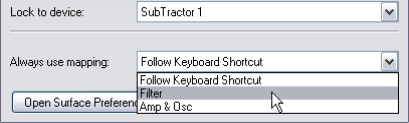
Locked devices (see “Locking a surface to a device”) can also be locked to a specific mapping variation.
|
For example, you could lock a control surface to control the Main Mixer, so you can always control overall levels while playing/tweaking other devices. See “Remote controlling the Main Mixer” for an example.
|
|
Control surfaces/keyboards that use the Easy MIDI Inputs function (see “Automatic set-up using the Easy MIDI Inputs function”) cannot be locked to devices.
|
|
|
If the selected control surface supports keyboard shortcuts for selecting mapping variations (see “About mapping variations”) an additional “Always use Mapping” pop-up appears.
|
The device is now locked to the selected control surface. In Remote Override Edit mode (see “Activating Remote Override Edit mode”) a locked device is shown with a lock symbol in the upper left corner of the device panel.
|
|
It’s also possible to lock a control surface to the ReGroove Mixer (see “The ReGroove Mixer”) to control its parameters via Remote!
|
|
|
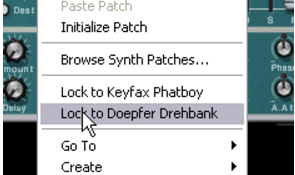
Another way to map parameters is to have “Remote Override Edit Mode” deactivated on the Options menu, and to simply right-click (PC) or [Ctrl]-click (Mac) on the parameter you wish to remote control.
|
You can also right-click (Win) or [Ctrl]-click (Mac) on the device panel to select the same item from the context menu.
|
|
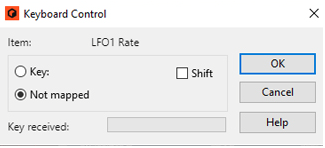
Another way to assign keyboard remote commands is to have “Keyboard Control Edit Mode” deselected on the Options menu, and to simply right-click (Win) or [Ctrl]-click (Mac) the parameter you wish to remote control.
|